ICT Market Tendencies
Russia no longer represents a major open market potential within EMEA due to international sanctions, the withdrawal of most Western technology vendors, and the country’s increasing isolation from global trade and finance. Although Russia continues to exert political and military influence in parts of Eastern Europe and Central Asia, its economic ties with Western markets have been drastically reduced.
Demographically, the country faces a declining and aging population, particularly outside major urban centers such as Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Despite this, the ICT sector remains strategically important for the Russian government, especially in the context of import substitution and digital sovereignty policies designed to replace Western technologies with domestic or “friendly nation” alternatives (notably from China, India, and Turkey).
The ICT ecosystem has therefore become more state-driven and inward-looking. Public institutions and state-owned enterprises now account for an overwhelming share of demand — more than two-thirds of total IT spending — focused on national infrastructure, cybersecurity, and local software development. Private investment has slowed, and international transparency has declined due to widespread grey-market practices and parallel import schemes.
Foreign vendors from the US and EU have largely exited the market, while Chinese and domestic suppliers have strengthened their positions. Hardware and telecom equipment increasingly come from Asia, and Russian software firms — notably in security and business applications — have gained ground domestically thanks to government support and currency devaluation.
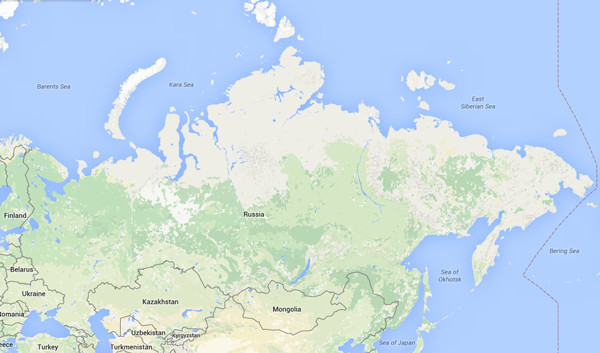
The regional distribution of ICT activity remains centered around the Central region (Moscow), which accounts for nearly 40% of active companies, followed by the Northern-Northwest region (Saint Petersburg) and the Ural industrial belt. Online sales and digital services are growing but remain constrained by logistics and payment-system limitations.
The Russian software industry retains strong technical expertise, especially in cybersecurity and system programming, but international cooperation and exports have diminished significantly since 2022. The market continues to face chronic issues such as piracy, a shortage of advanced components, and delays in digital infrastructure modernization.
Overall, the Russian ICT market has transitioned from a fast-growing, internationally integrated economy to a restricted, state-controlled, and domestically focused environment, dependent on parallel imports and alliances with non-Western partners.

Database Russia - Click on any cell in the table to see the corresponding selection- Note that due to 2022 events the data update has been put on hold
FURTHER SOURCES OF INFORMATION
OCS Distribution ; MERLION
IT Channel Press & Players:
CRN Russia
Public organisations & Useful Associations:
Russian Information & Computer Technologies Industry Association (APKIT) ; Institute of the Information Society


 Consulting Services
Consulting Services